Automate inputs
Autocomplete values
Use parameter suggestions to help users enter a correct value. For instance, when entering a product name, it might make sense to dynamically query a database for values starting with the already entered text, and suggest to auto-complete the value.
Suggestions are functions that take one string argument, and return a list of strings to be suggested to user. Suggestions work only for string parameters.
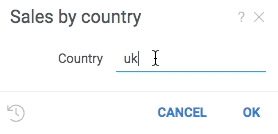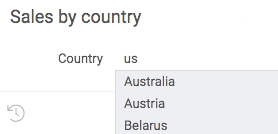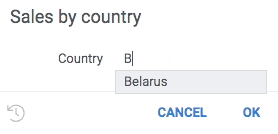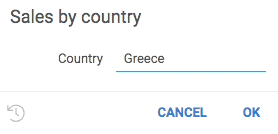
The following example helps user enter a country name by dynamically retrieving a list of names from a web service:
- Result
- Register suggestions
- Use suggestions
grok.functions.register({
signature: 'List<String> jsSuggestCountryName(String text)',
isAsync: true,
run: async function(text) {
let response = await fetch('https://restcountries.eu/rest/v2/name/' + text);
return response.status === 200 ? (await response.json()).map(country => country['name']) : [];
}
});
#name: Sales by country
#language: python
#input: string country = uk {suggestions: jsSuggestCountryName}
The same concept could be used for SQL queries:
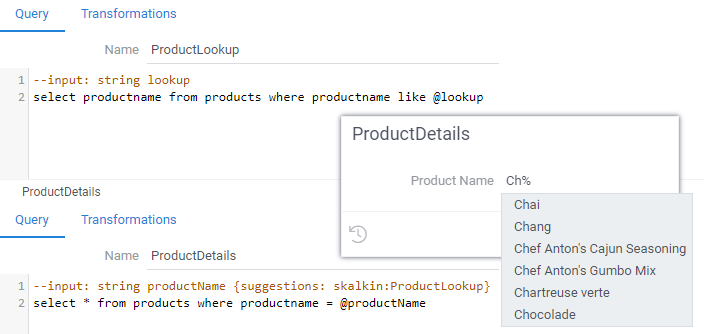
Precalculate inputs
Use parameter editor to set the output of another function to the parameter value.
//input: dataframe table {editor: Package:DataQuery}
//input: dataframe table {editor: Package:DataQuery(1, "France")}
Here, Datagrok will execute the Package:DataQuery function right before your script and pass the output table to the
script as an input parameter.
//input: dataframe table {editor: PowerPack:DataQuery; editor-button: Outliers...}
Specify the editor-button parameter to add a button that executes your subfunction separately and allows the user to
check the output before starting the script.
Suggest choices
Use choices to provide the editor a list of values to choose from. When choices are provided, the editor becomes a combo box. Choices can be either a fixed list, or a function that returns a list.
A choice provider is a function with no parameters that returns a list of strings.
The following example demonstrates two ways of defining choices:
- Result
- Register choices
- Use choices
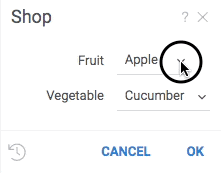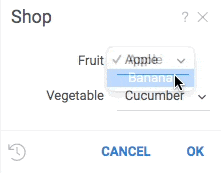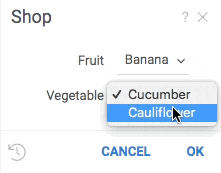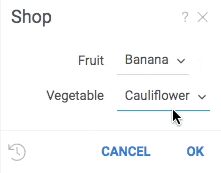
grok.functions.register({
signature: 'List<String> jsVeggies()',
run: () => ["Cucumber", "Cauliflower"]});
#input: string fruit {choices: ["apple", "banana"]}
#input: string vegetable {choices: jsveggies}
Validate inputs
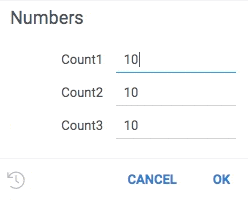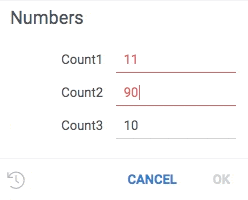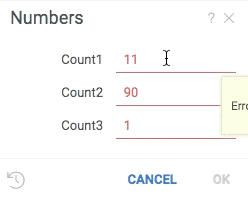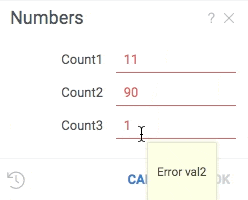
Validators check whether the value falls in the expected range, and provide visual cue if it does not. To add a validator to a parameter, provide a comma-separated list of functions that will be invoked each time a value is changed. A null indicates that the value is valid, anything else indicates an error which gets shown to the user.
A validator is a function that accepts one parameter of any type and returns a string. Choice providers are applicable only to string parameters.
- Result
- Register validators
- Use valdiators
grok.functions.register({
signature: 'List<String> jsVal1(int input)',
run: (input) => input < 11 ? null : "Error val1" });
grok.functions.register({
signature: 'List<String> jsVal2(int input)',
run: (input) => input > 9 ? null : "Error val2" });
#name: Numbers
#language: python title="Use registered validators"
#input: int count1 {validators: ["jsval1", "jsval2"]} [Number of cells in table]
#input: int count2 {validators: ["jsval1"]} [Number of cells in table]
#input: int count3 {validators: ["jsval2"]} [Number of cells in table]