Jupyter Notebook
The Jupyter Notebook is an open-source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. Uses include data cleaning and transformation, numerical simulation, statistical modeling, data visualization, machine learning, and much more.
Datagrok lets you create, edit, import, link, and apply Notebooks into tables.
Create a notebook
There are several ways to create a new notebook:
- From the Top Menu, select ML > Notebooks > New Notebook..
- Go to Browse > Platform > Notebooks and click NEW NOTEBOOK from the notebook toolbar.
- Run
CmdNewNotebook()from the Console. - Select a table and click Actions > Open in Notebooks in the Context Panel.
- Right-click the table's header and select Table > Open in Notebook.
If you want to link a notebook to a table, use one of the last two methods.
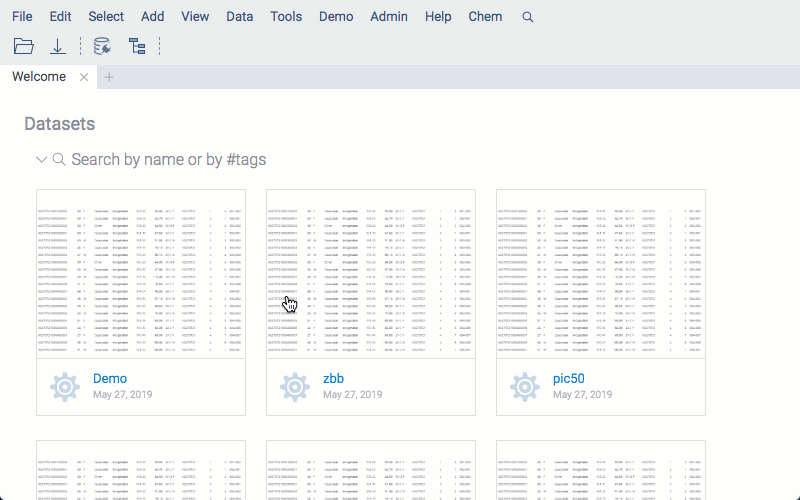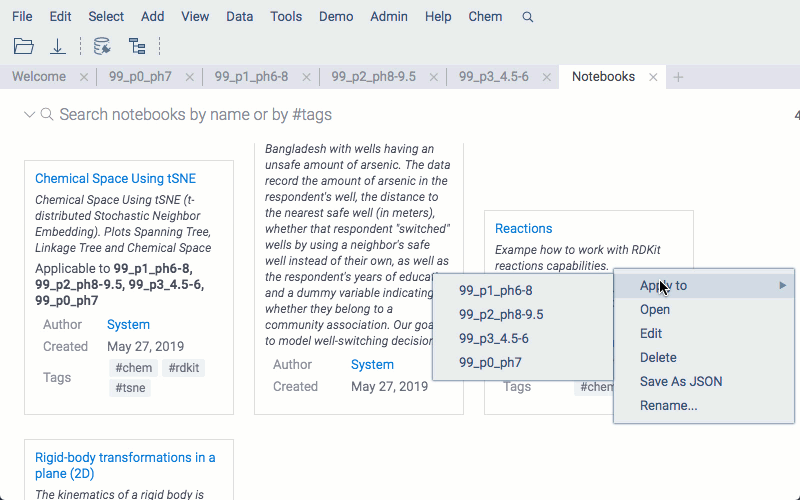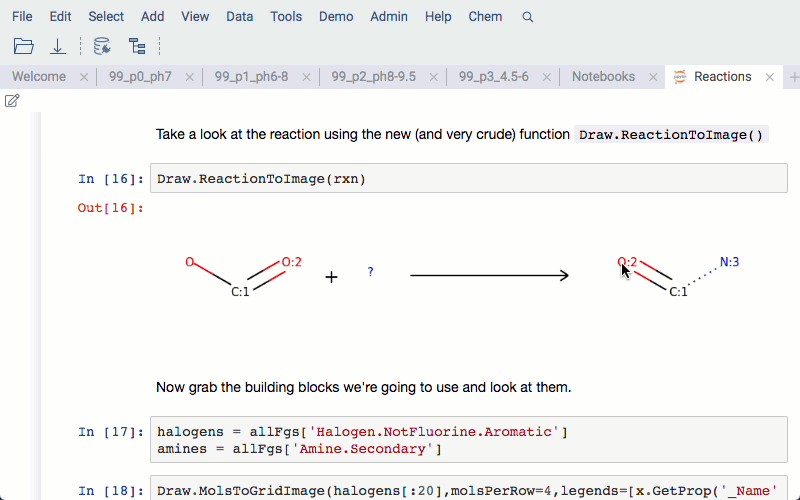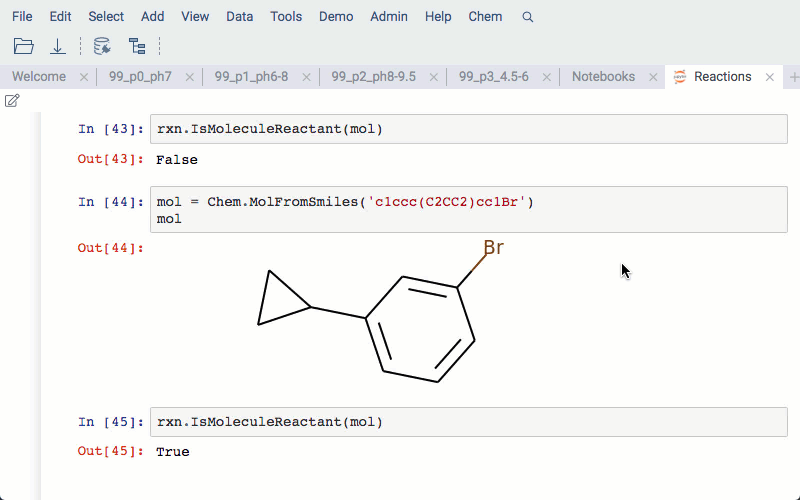
Notebooks browser
In the Notebooks Browser, you can navigate over all available notebooks. If a notebook can be applied to any of the opened tables, an Apply to option will be available in its context menu.
Apply existing notebooks into tables
To use one of the notebooks available in the platform, open a table and search for applicable notebooks in the Notebooks Browser. Select a notebook and use its context menu to apply it to your data.
Return a table into the platform
Use simple function called "grok". Example:
grok(< table >)
where table in a Pandas dataframe.
Supported language
- Python (3.8)
Environments
Each script can be run in an isolated environment, with predefined packages configuration, same as for Script Environments. The environment can be specified in the notebook properties.
Importing notebooks
To import a notebook, just drag-and-drop the corresponding .ipynb file to the platform or use
import.
Videos
See also: