Access control
Datagrok provides robust security through its authentication, authorization, and credential management systems. These features control access to functionalities and data within the platform, ensuring that only authorized users can operate within their granted permissions.
Authentication
Authentication is verification of identity by providing credentials. Datagrok supports the following authentication methods:
- Internal (login/password): Sign in with a username and password
- OAuth: Sign in using Google, Facebook, GitHub, or OpenID accounts
- Single Sign-On (SSO): Custom SSO for enterprise customers
- OpenID: Sign in using OpenID providers like Azure AD
You can enable all methods separately or combined. After successful authentication, Datagrok issues a session token for subsequent API calls, ensuring continuous secure access during the session.
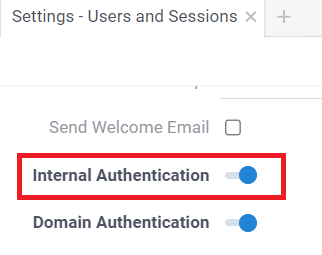
To set up authentication, go to Sidebar > Settings () > Users and Sessions. For detailed instructions, see Configure authentication.
If you disable the login/password authentication (for example, after setting up the SSO), the platform will no longer accept logging in with the username/password, so be careful to not lock yourself out and make sure SSO works.We recommend to check that SSO works by signing into Datagrok using incognito mode before disabling the login/password authentication.
If you don't provide a functional alternative before disabling the login/password authentication, this may require a platform redeployment to regain access.
Login-password authentication
Datagrok uses a user name and password to authenticate users. Passwords are salted with random data and encrypted with the 1024xSHA-256 algorithm, ensuring they cannot be read from the system.
When a user logs in, the user name and password pair is passed to the server. If
the password hash matches the stored hash, a session token is generated. Every
subsequent API call must be made with the Authorization: token HTTP header,
where token is the session token. This token becomes invalid after logging out.
Datagrok doesn't store user passwords after login. If a user forgets their password, the only way to regain access is to reset the password using the link on the login form or for the Datagrok Administrator to reset the password.
Authorization
Authorization in Datagrok is based on Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and determines whether a specified user can execute a specified operation against a specified entity. This is achieved by defining user groups and associating them with permissions for different entities.
Permissions
When you create an entity, only you (its author) can access it initially. To grant access to others, you need to share it and assign permissions:
Common Entity Permissions
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| View | See and open the entity; read basic attributes |
| Edit | Modify entity attributes |
| Delete | Delete the entity |
| Share | Change entity permissions |
Data Connection Permissions
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Connection Query | Execute any query on the data connection |
| Get Schema | Read database schema |
| List Files | List files on the file connection |
Data Query Permissions
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Execute Data Query | Execute the query |
Table Permissions
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Read Table Data | Read table data |
All permissions are grouped in two categories:
- View and Use: Includes only the View permission and all entity-specific use permissions
- Full control: Includes all permissions
Entity permissions are granted to groups rather than individual users, which simplifies security administration. For convenience, Datagrok automatically creates a "personal group" for every user in the system, named after the user.
Permission sets assigned to a group are inherited by all members of the group. Groups can be nested, allowing members of a child group to inherit permissions set for a parent group. However, circular membership is forbidden.
To fully control access to external data sources (like file shares or databases), you can also associate groups with credentials
Global Permissions
Global permissions define system-wide capabilities in Datagrok. They can be assigned to roles, users or groups. These permissions control what users can create, administer, or view across the entire platform.
Permission for admin actions:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Create User | Create a new user from Users list or with API |
| Edit User | Edit a user from Users list or with API |
| Edit Group | Edit any user group, add or remove members |
| Edit Global Permissions | Edit this list of permissions |
| Start Admin Session | Ability to temporarily disable permissions check |
| Edit Plugins Settings | Change Datagrok server-side settings |
| Publish Package | Install a package or deploy with Datagrok tools |
| Delete Comments | Delete comments in any chat inside Datagrok |
| Admin System Connections | Edit system data connections such as System:AppData or System:Datagrok |
| Admin Sticky Meta | Ability to set up Sticky Meta |
| Create Repository | Register a new package repository |
| Create Group | Create a new user group |
| Create Role | Create a new user role |
Permissions to create entities:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Save Entity Type | Create or edit Entity Type for Sticky Meta |
| Create Entity | Create any entity within Datagrok |
| Create Script | Create a script |
| Create Security Connection | Create a connection that provides credentials |
| Create Database Connection | Create a connection to a database |
| Create File Connection | Create a file share |
| Create Data Query | Create a new data query |
| Create Dashboard | Create a new dashboard |
| Create Space | Create a new space |
General permissions:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Invite User | Invite a new user by email, explicitly or by sharing something |
| Share With Everyone | Share something with someone the user has no common groups or roles with |
| Send Email | Send email to any user using group emails |
Permissions to show or hide nodes in Browse Panel:
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| Browse File Connections | Show Files section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Database Connections | Show Databases section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Apps | Show Apps section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Spaces | Show Spaces section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Dashboards | Show Dashboards section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Plugins | Show Plugins and Repositories sections in Browse Panel |
| Browse Functions | Show Functions section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Queries | Show Queries section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Scripts | Show Scripts section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Open API | Show Open API section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Users | Show Users section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Groups | Show Groups section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Roles | Show Roles section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Models | Show Predictive Models section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Dockers | Show Dockers section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Layouts | Show Layouts section in Browse Panel |
| Browse Shared Data | Show Shared Data in Browse Panel |
You can set Datargok global permissions as a part of GROK_PARAMETERS. Get the template JSON in /settings view using {} button near the server settings section.
Put any parameter to settings map of GROK_PARAMETERS respecting the hierarchy.
See also: Configuration
Credentials management system
Datagrok provides a built-in credentials management system that securely stores and protects data connection and plugin credentials.
Credentials contain sensitive information used to connect to data sources, such as login/password pairs for databases or tokens and private keys for webservices.
Each credential is associated with a group and a connection or a plugin. When a user accesses the entity, the system automatically selects the appropriate credential based on the user's group membership.
Depending on the connection, the call to the external service is performed either on the server or the client side. For client-side calls, the credential are retrieved from the server. Some connections, such as databases, are intended to be accessible only from the server side. In such cases, set the Requires Server flag to true (accessible via the Edit... command) to prevent the retrieval of credentials by the client.
Credentials storage
To enhance security, all external credentials are stored in a separate database and encrypted with a platform key generated during deployment. Even if one of the systems is compromised, an attacker still won't be able to access the credentials.
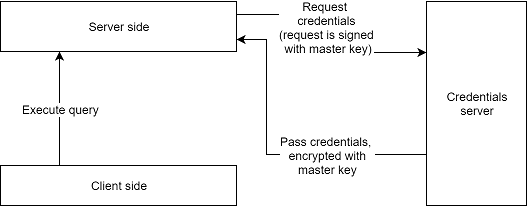
If your organization already uses a specialized credential vault like AWS or GCP Secrets Manager, you can configure Datagrok to use it.
To store credentials in Datagrok's credentials storage programmatically, send a POST request to $(GROK_HOST)/api/credentials/for/$(ENTITY_NAME) with a raw body containing JSON, such as {"login": "abc", "password": "123"}, and headers {"Authorization": $(API_KEY), "Content-Type": "application/json"}. Take the API key from your profile page in Datagrok, e.g., https://public.datagrok.ai/u.
See this sample:
To add credentials from the UI:
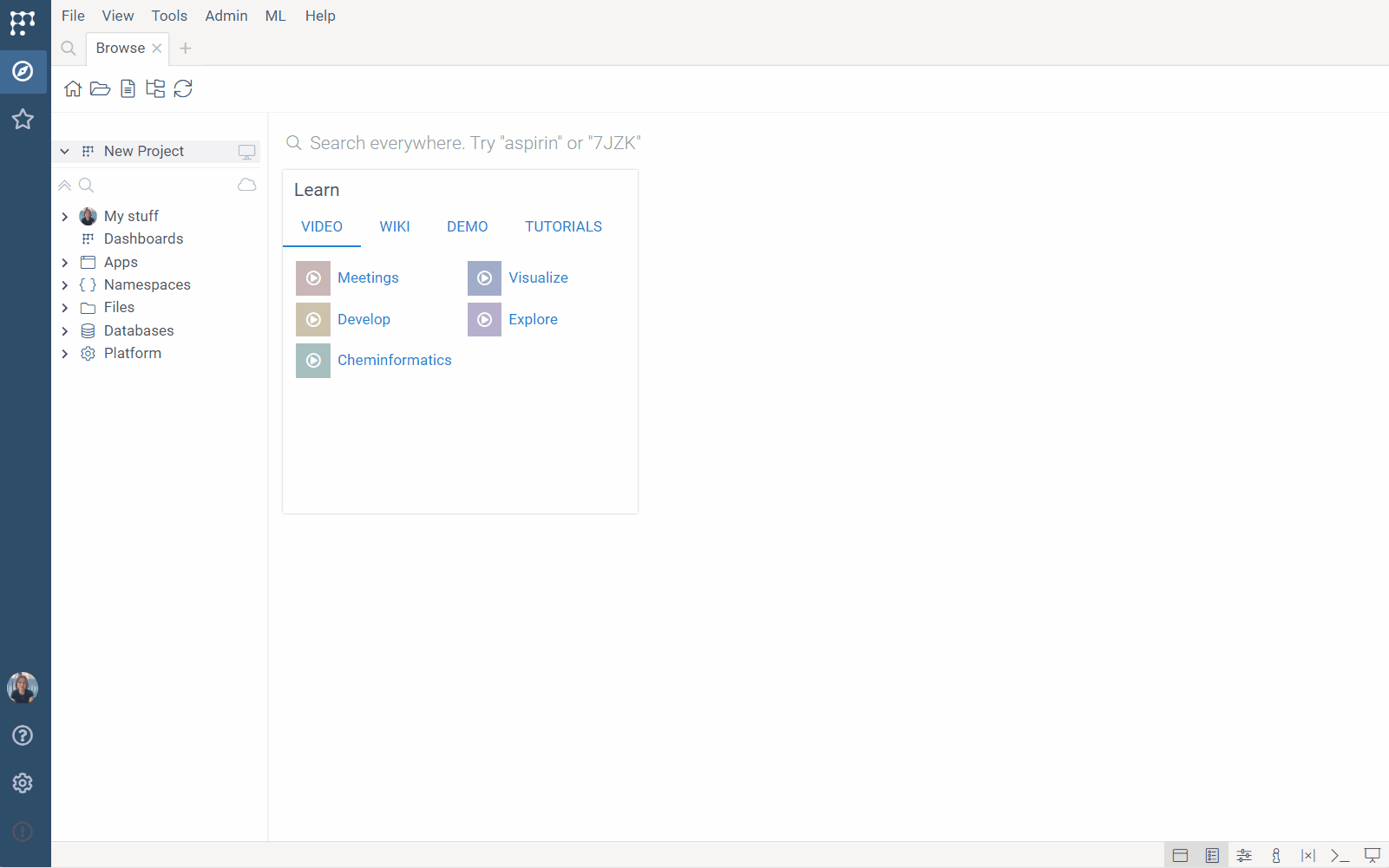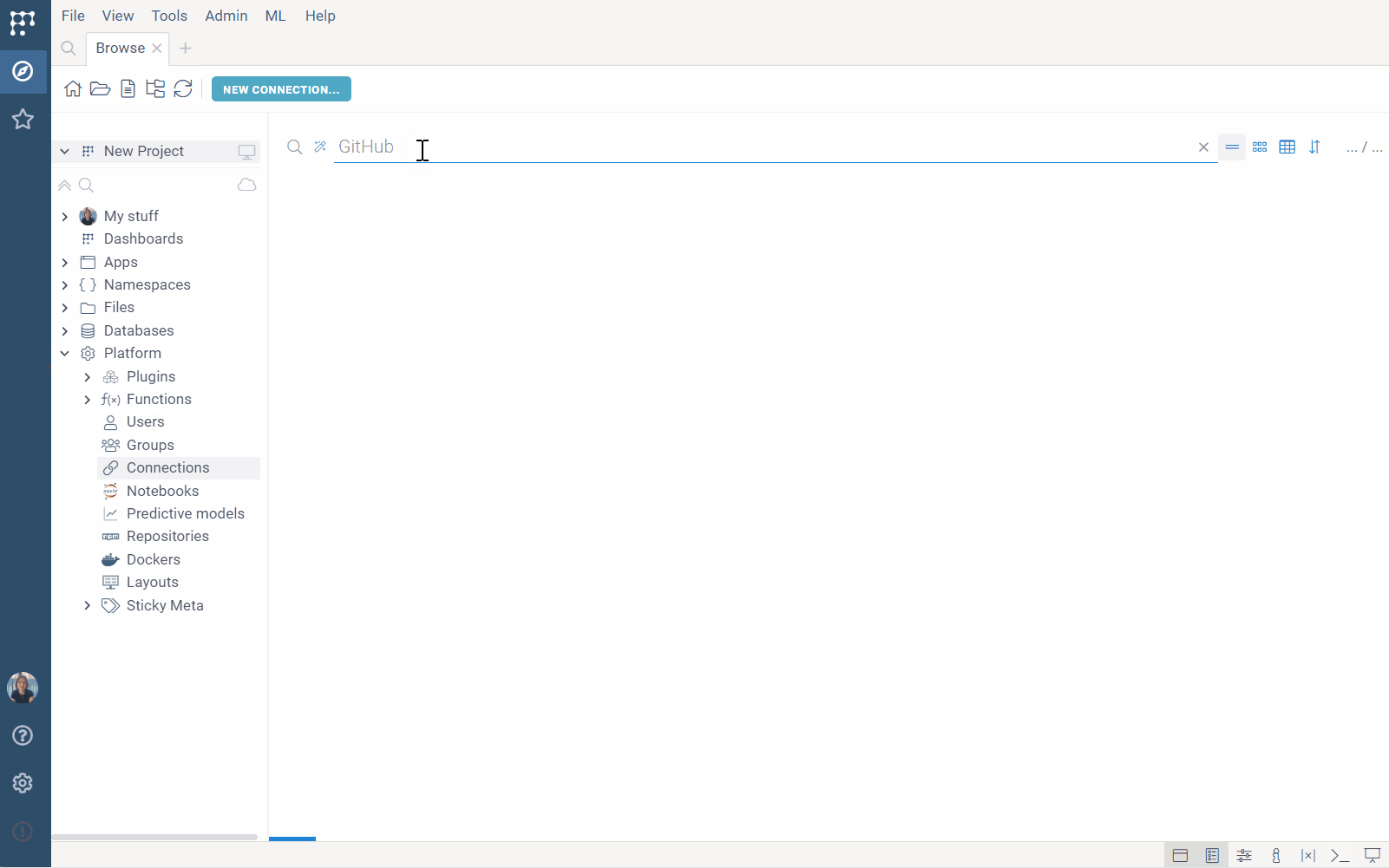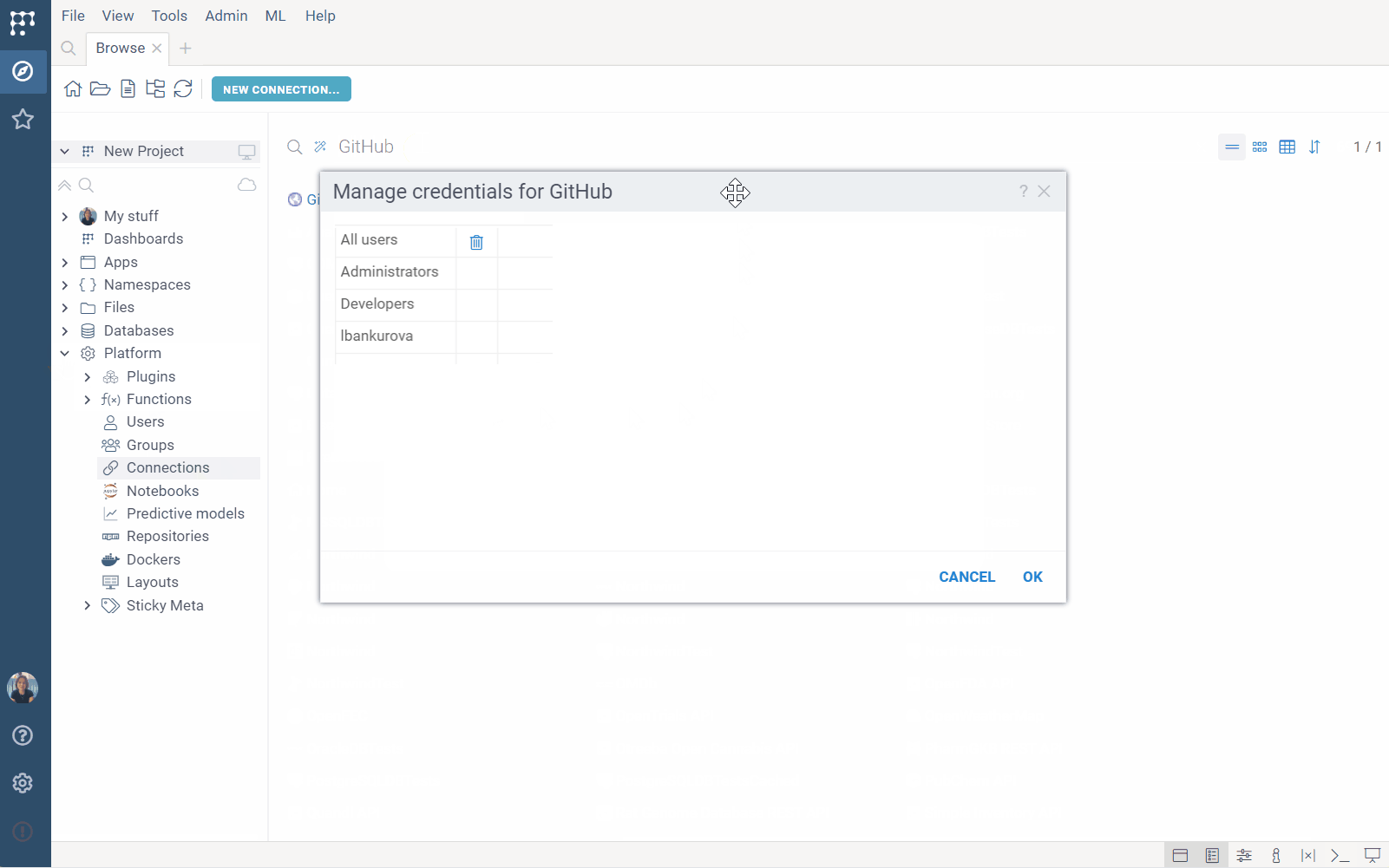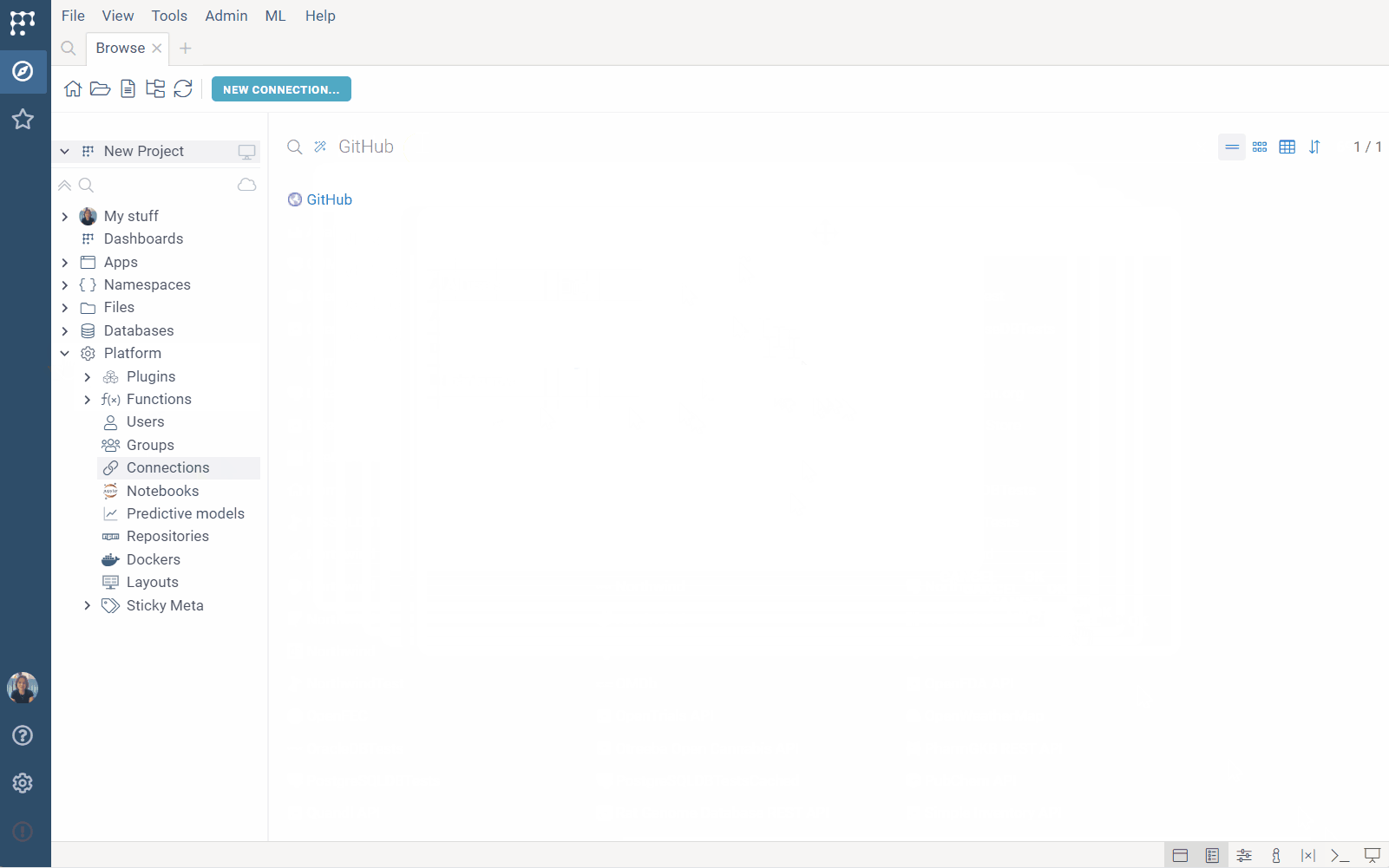
- From the context menu, select Credentials.... The Manage credentials dialog opens.
- In the dialog, click the group and enter appropriate credentials in the fields provided.
Note: The dialog only shows the groups you belong to. To assign credentials for the All users group, you must have permissions to edit the connection. To assign credentials for other groups, you must both have permissions to edit the connection and be that group's admin.
- Click OK.