Project
Project is a collection of entities along with the applied visualizations. Projects are used to group and share data and other assets with other users. One of the most common applications of projects are dashboards that consist of tables ( with either static or dynamic data), and visualizations applied to them.
Uploading a project
Creating a project is easy. After getting the data of interest in the scratchpad project in workspace,
click on the UPLOAD button. After the project gets uploaded to the server, a separate window pops us asking you whom
to share the project with. By default, it is only accessible by you, you have to share it in order for others to use it.
Or, if you are editing an existing project, click SAVE to save your changes.
Use Share context action to edit access permissions. Sharing a project will automatically share all entities and data
inside.
Dynamic data
Whenever a table is created by executing a function (such as a database query), this information gets stored with the table as a "generation script". This serves multiple purposes:
- Provides data lineage
- On-demand data refreshing (Table toolbox, "Query" panel,
REFRESHbutton) - Enables publishing dashboards with the dynamic data
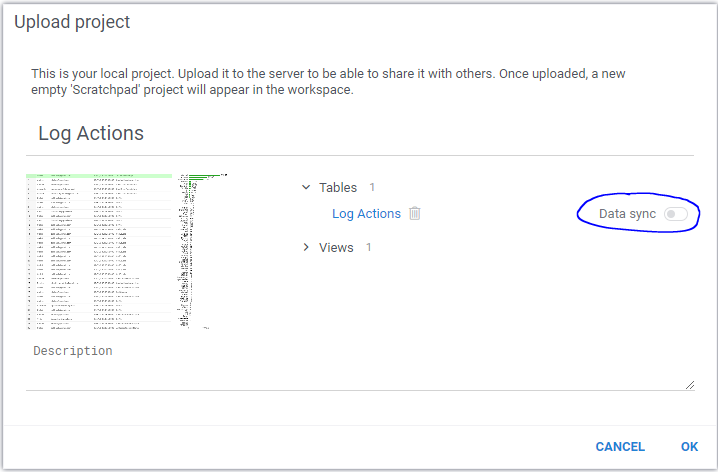
In the "Upload project" dialog, a "Data sync" option appears next to the tables that have a generation script defined. This option determines whether the data should be stored as a static snapshot, or as a generation script. In the latter case, the function will be re-executed whenever the project is opened.
Project types
Projects are organized in a tree structure. Rights on particular entities are inherited based on this
hierarchy. There are two main types of projects: root and regular. Root projects can contain one or more non-root
projects, for example, the link Demo:CoffeeCompany
indicates that the CoffeeCompany project is part of the root project Demo. Any link to an entity on the platform
starts with the root project. And since an entity can have only one canonic address, other related projects will
reference the link rather than the entity itself. This fact becomes important in the context of regular projects. As the
name suggests, they are the most common ones
(that's what users create by default). Entities from such a project belong to the higher-level namespace, which means
they are tied to the root project. To find out where an entity comes from, see Links in the Details tab of the
context panel.
Root projects are automatically created for users and packages. When the user uploads a project, it gets saved to their namespace. However, the existing entities will be available in the user's project via link. As for packages, each version has its own project, which allows sharing packages on a version level.
Project gallery
Browse projects that are available to you. Use Smart search for powerful filtering capabilities.
Click on the context menu to the left of the search box to control sort order, as well as access your recent searches.
Controls:
| Click | Show in context panel |
| Right click | Context menu |
| Double click | Open |
Filtering
The following fields could be used to filter projects with smart search:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| name | |
| description | |
| createdOn | |
| updatedOn | |
| author | User object |
| starredBy | User object |
| commentedBy | User object |
| usedBy | User object |
Resources
YouTube videos:
Dynamic Dashboards
Building dynamic dashboards using database queries