Develop custom filters
Developers can extend Datagrok with custom filters. This could be done by defining a class that extends DG.Filter class. An example of such class can be found in the Widgets package.
The filter then must be registered in the package.js file:
//name: Single Choice
//description: A filter that lets you select exactly one category
//tags: filter
//output: filter result
export function radioButtonFilter() {
return new RadioButtonFilter();
}
If you are on version ^4.12.x of datagrok-tools, you can use class decorators to register filters:
@grok.decorators.filter({
semType: 'Country',
})
export class RadioButtonFilter extends DG.Filter {
/* RadioButtonFilter contents */
}
This is equivalent to adding a function to package.ts. There is no need to add anything other than the class itself.
When you run the build script for your package, the webpack plugin called FuncGeneratorPlugin will add a special
package.g.ts file to your project. Note that it is not on the ignore list, so you are supposed to commit this file.
The filter then can be invoked in the package with JS API as shown in custom filters example:
let tv = grok.shell.addTableView(grok.data.demo.demog());
tv.filters({filters: [
{type: 'Widgets:radioButtonFilter', columnName: 'race'},
]});
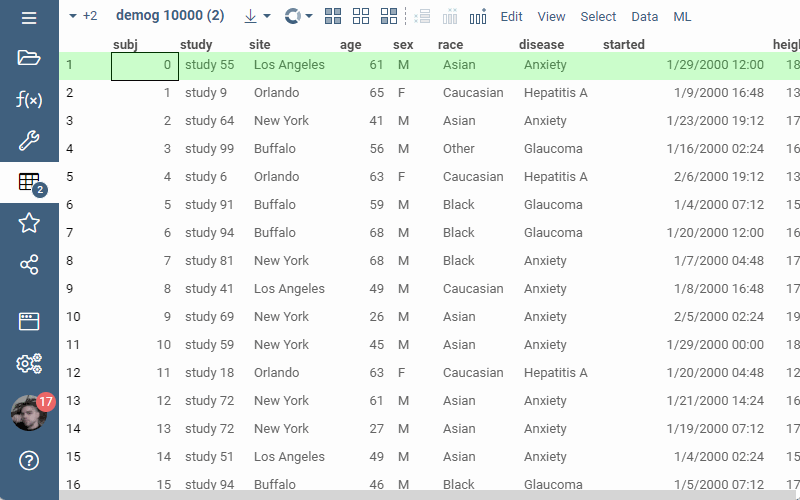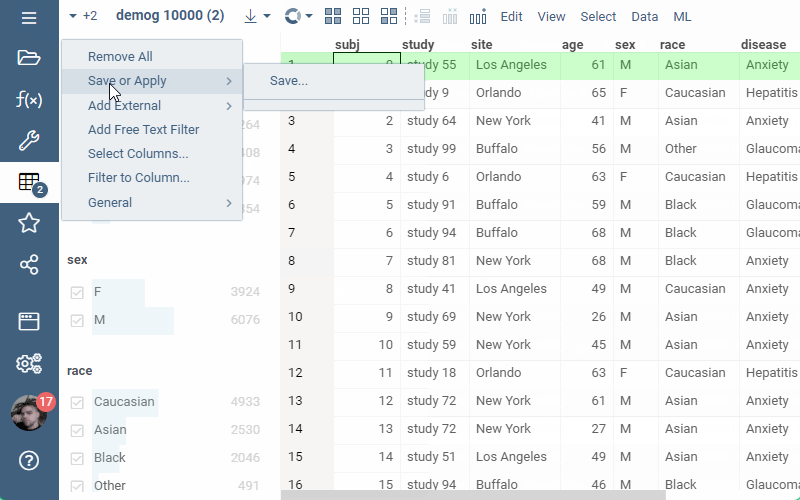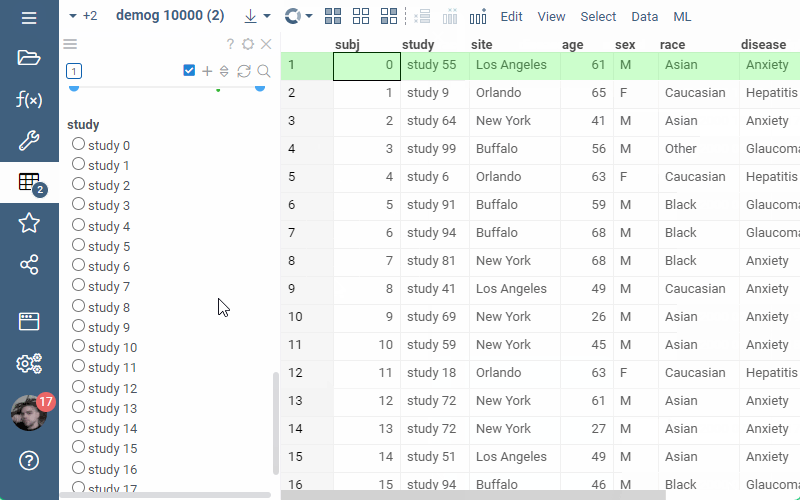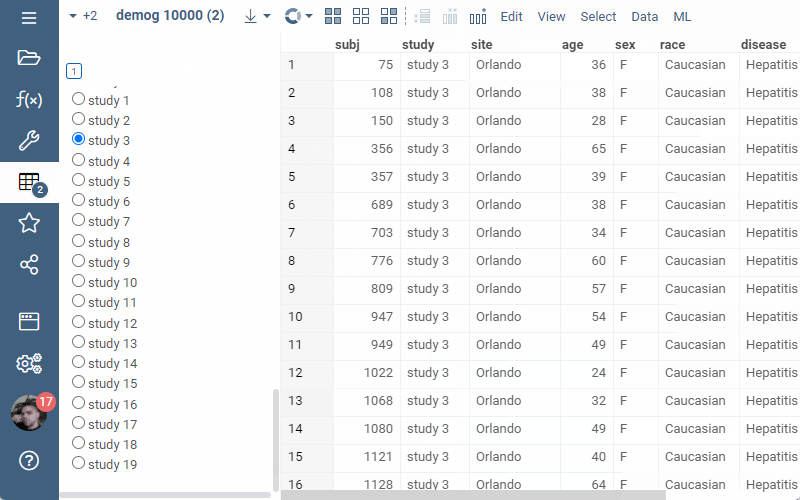
Or, alternatively, the filter can be added through UI:
See also: