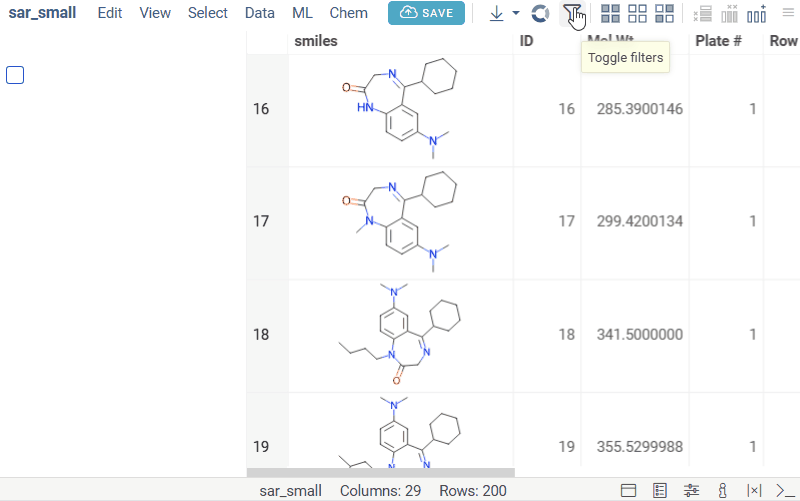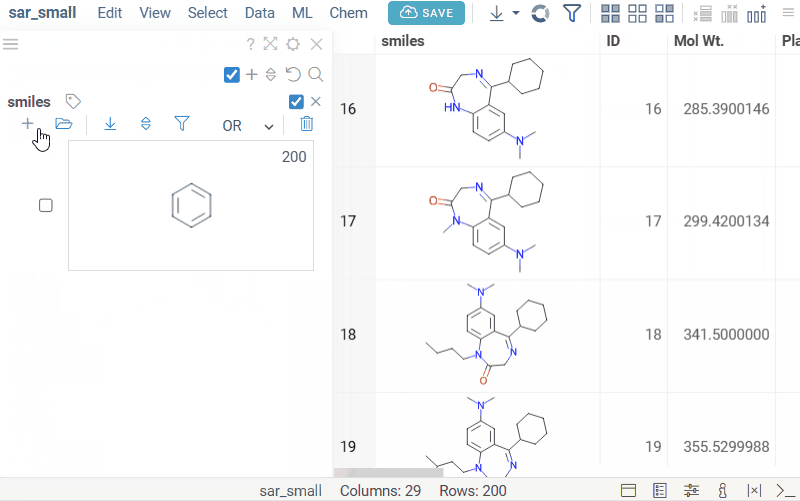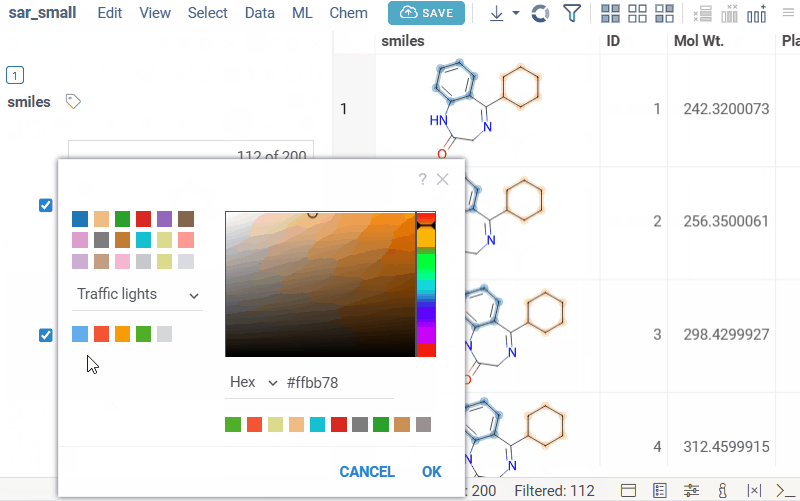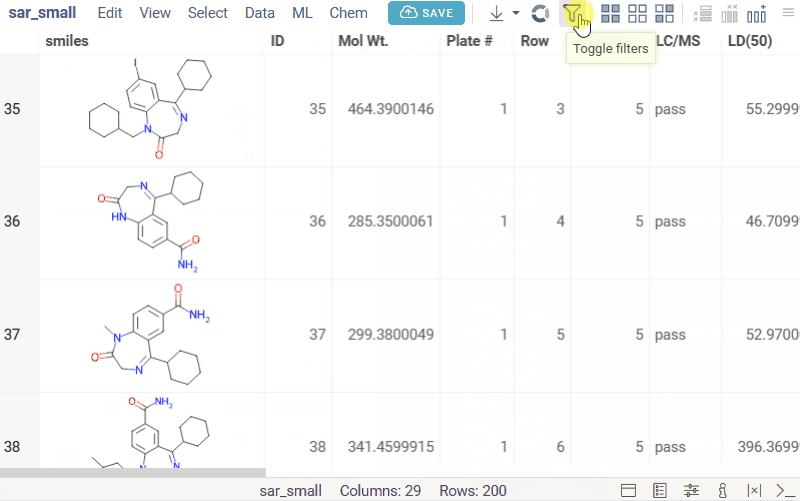
Filters
A set of controls for quick filtering, selection, and visual assessment of column values.
General:
| 1st column click | Toggle filter |
| 2nd column click | Toggle selection |
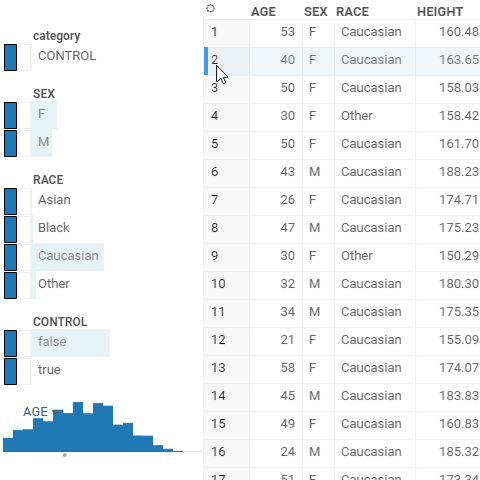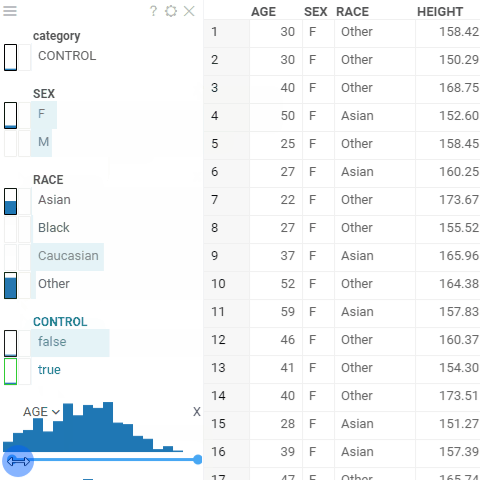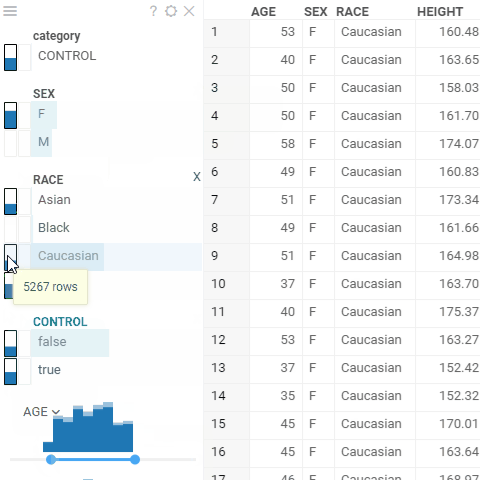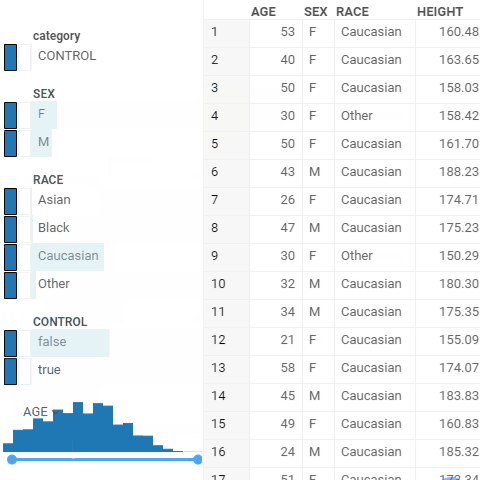
| Name column click | Filter by that category |
| Up / down | Filter by that category |
| Esc | Reset filter |
Search
Each categorical filter group has a search field for filtered values. Click the Search icon to the right of the filter caption to open it. This icon appears when you hover the mouse over the filter.
If you start typing text in the field, the filter will show all values that partially contain this text. But if you are typing words, separating them with a comma, then the filter will show only those values that exactly match each other.
It is also allowed to paste multi-line text from the clipboard into the search field. In this case, the filter will also display those values that exactly match each word. The checkbox on the left of the search field controls weather to select filtered out values only. If this checkbox is enabled, upon searching for value (or values), filter will automatically select only those values that match the search criteria. In contrary case if the checkbox is disabled, search will only filter out values and not select them.
Structure filter
Structure filter lets you filter molecules by structural patterns or similarity. It works on molecular columns and supports the following search types:
- Contains: filters molecules that contain the sketched structure.
- Included in: filters molecules where the sketched structure is a superstructure.
- Not contains: filters out molecules that contain the sketched structure.
- Not included in: filters out molecules where the sketched structure is a superstructure.
- Exact match: filters molecules that exactly match the sketched structure.
- Similar: filters molecules similar to the sketched structure; supports a similarity threshold.
To quickly filter the dataset by the selected molecule, right-click the molecule cell in the grid and select Current value > Use as filter.
Categorical mode
You can switch the structure filter to categorical mode, which treats each unique molecule as a separate, selectable category in the Filter Panel. To do that, click the column header, go to the Context Panel > Chemistry > Rendering, and set Filter type to Categorical. Alternalively, use column tags to set the categorical structure filter mode.

Scaffold tree filter
Scaffold tree filter lets you filter molecules based on their scaffolds.
The scaffold hierarchy is displayed as a tree, where you can:
- Select one or more scaffolds to filter the dataset.
- Switch the AND/OR control to define filter logic.
- Exclude selected scaffolds using the ≠ icon.
- Color scaffolds to highlight relationships; colors are shown in both the dataset column and the scaffold tree.
Bio substructure filter
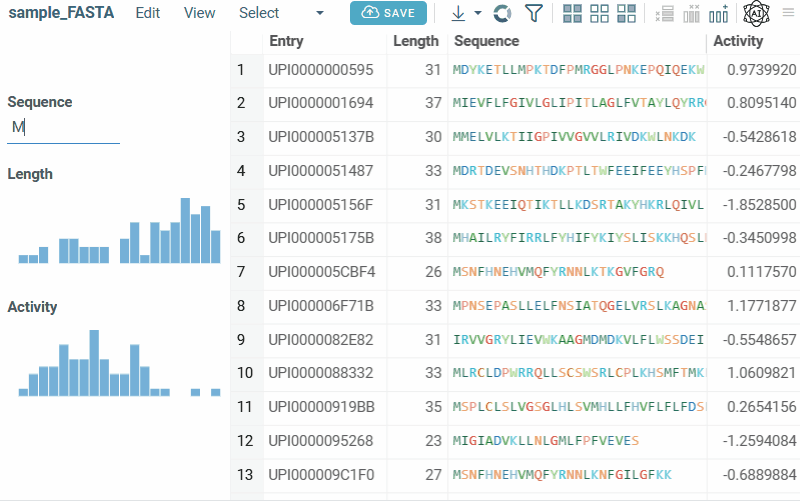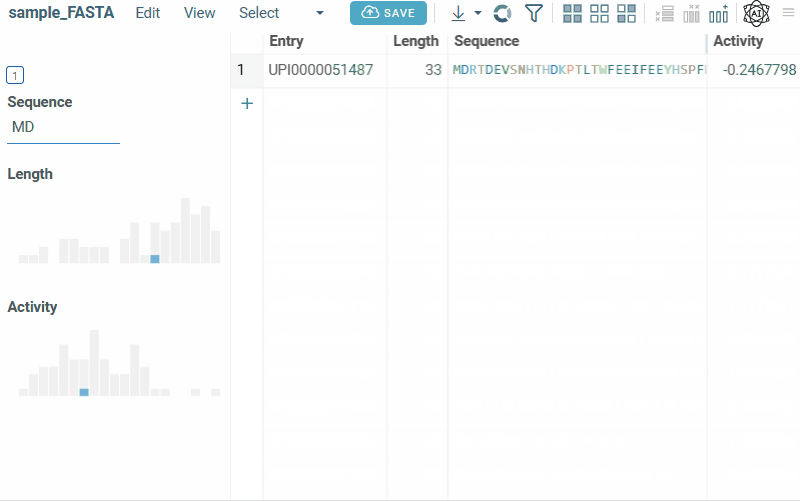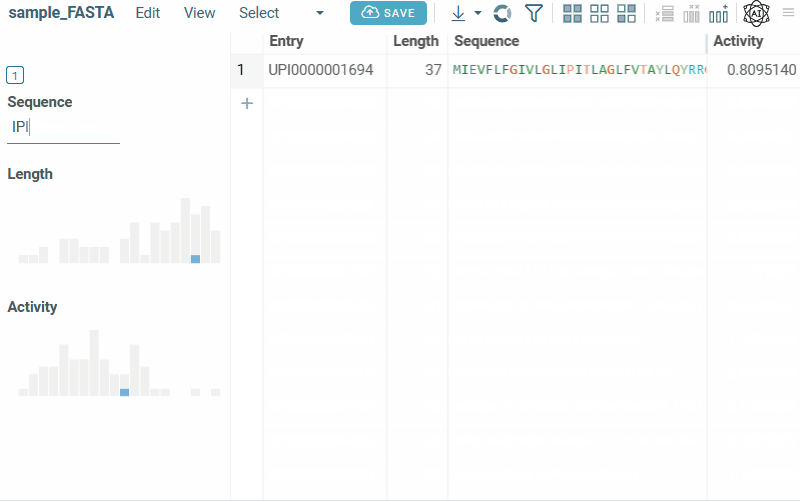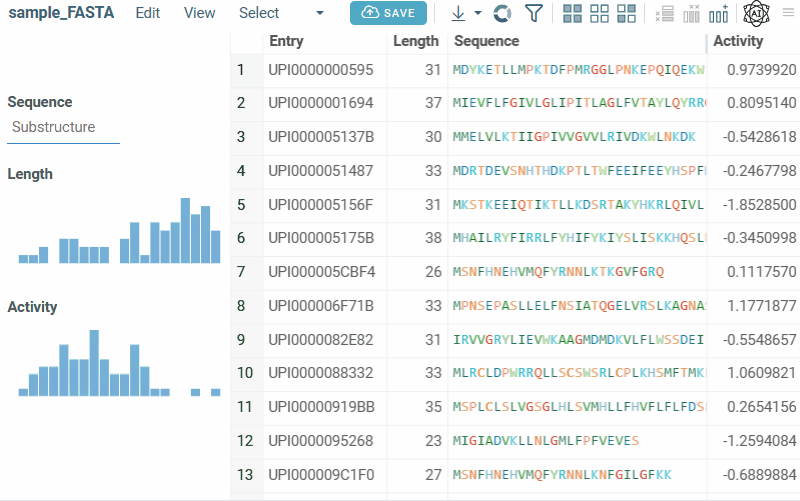
Bio substructure filter lets you filter macromolecules based on their subsequences:
- FASTA sequences: enter a subsequence.
- Separator-based sequences: enter a subsequence and specify the separator for exact matching.
- HELM sequences: use the visual editor to design complex structures for monomer-level filtering.
- FASTA
- Separator
- HELM
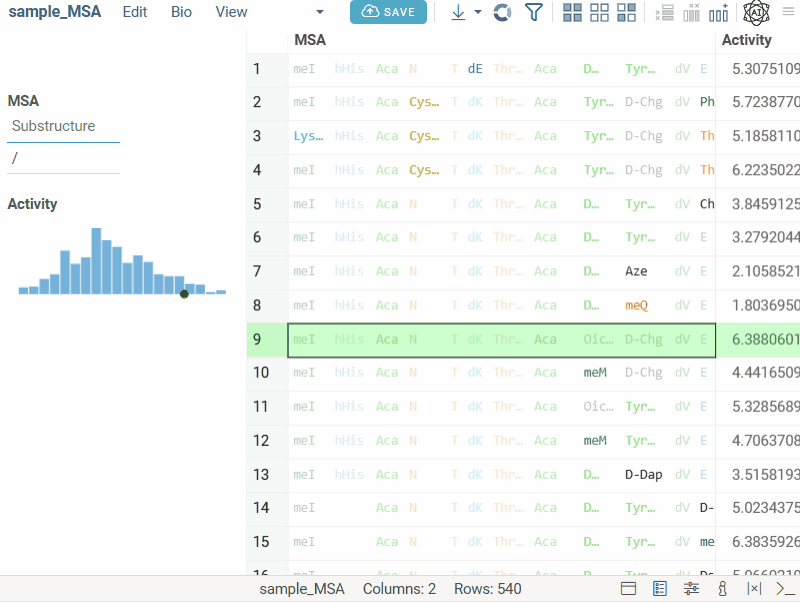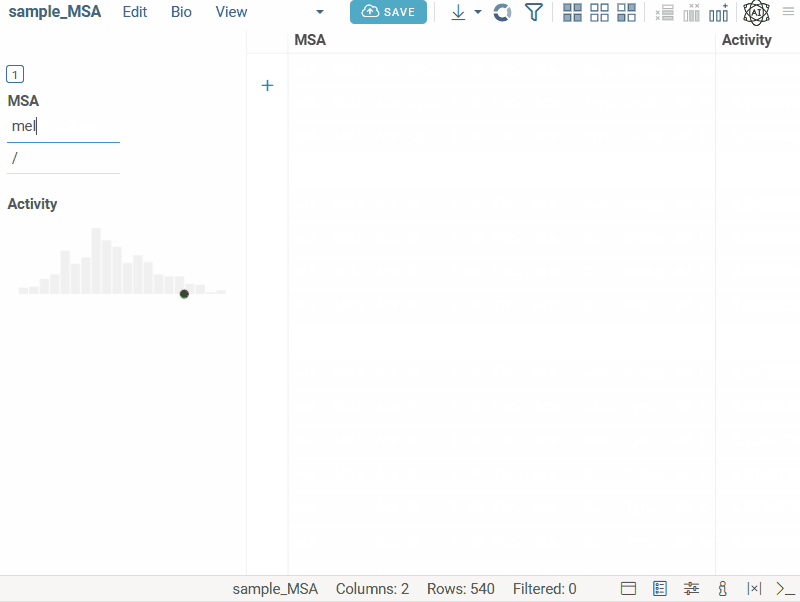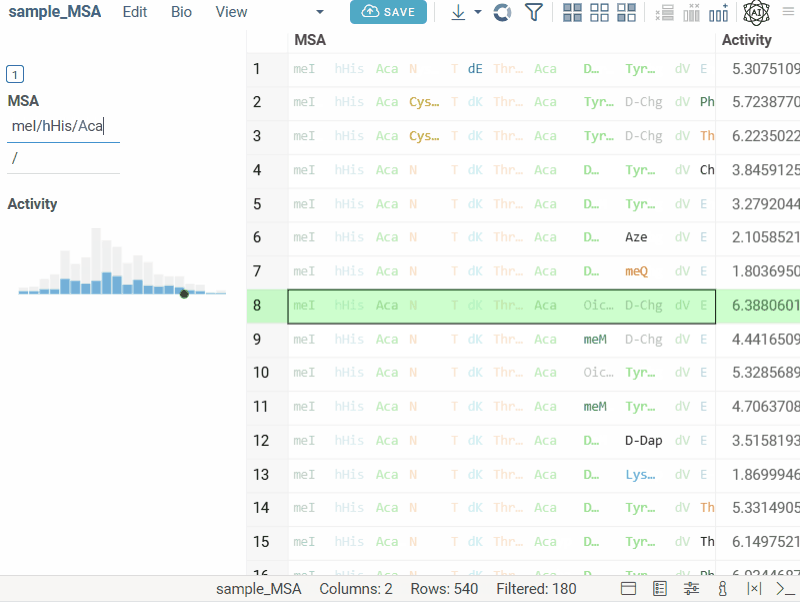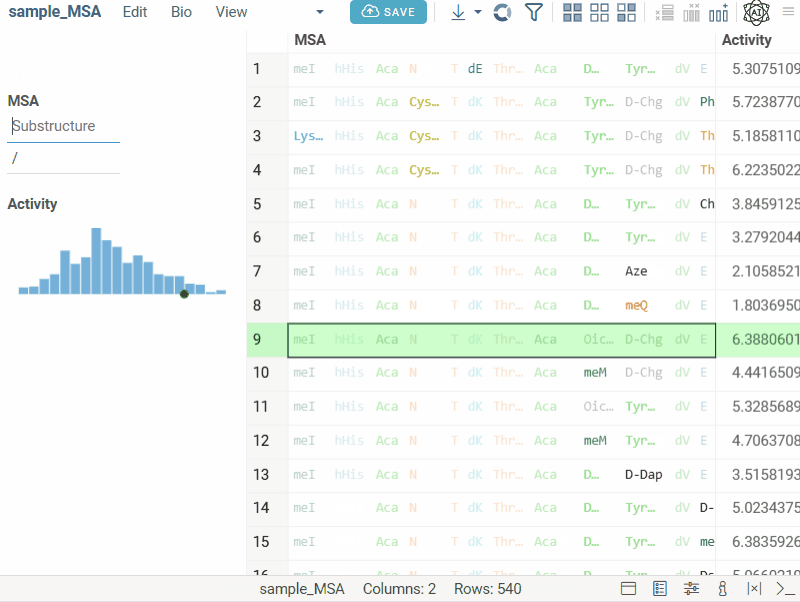

Text filter
This filter is used for fuzzy searching for the specified search terms, and applies to string columns that have the "Text" semantic type.
To add a search term, enter it in the search box, and press Enter. Use the checkboxes and the "and/or" switch to control search results. And/Or switch is used to control the logical operation between the search terms. To control the fuzzynes of the search, use the slider at the bottom of the search box. By default, the fuzzynes value is set to 0, which corresponds to the exact match. The higher the fuzzynes value, the more fuzzy the search will be. All the exact matches from the filter will be highilghted in the column values.

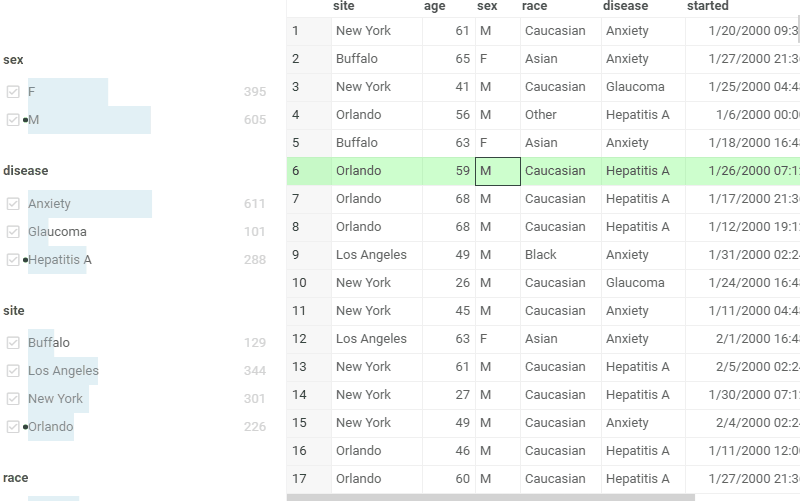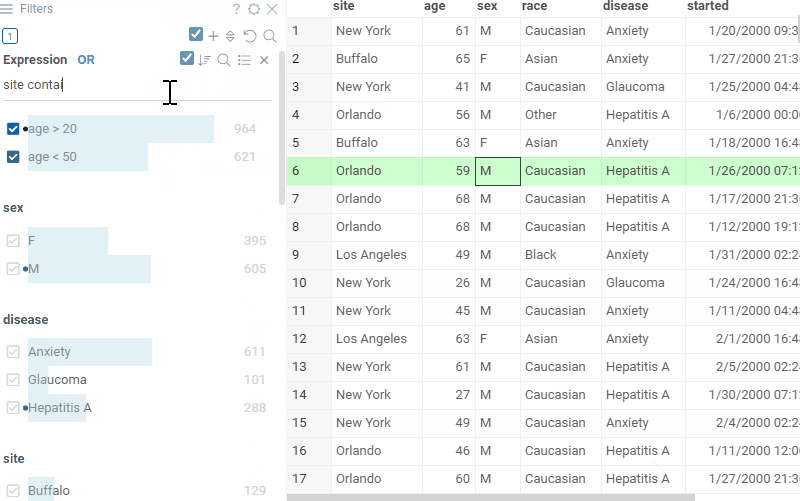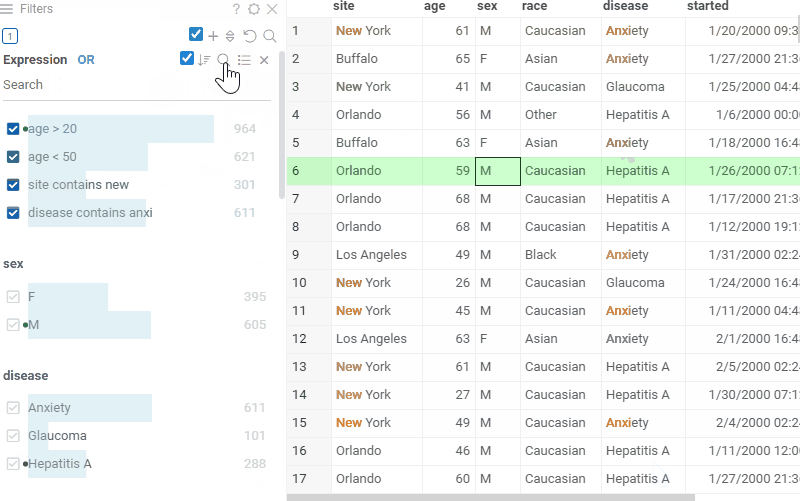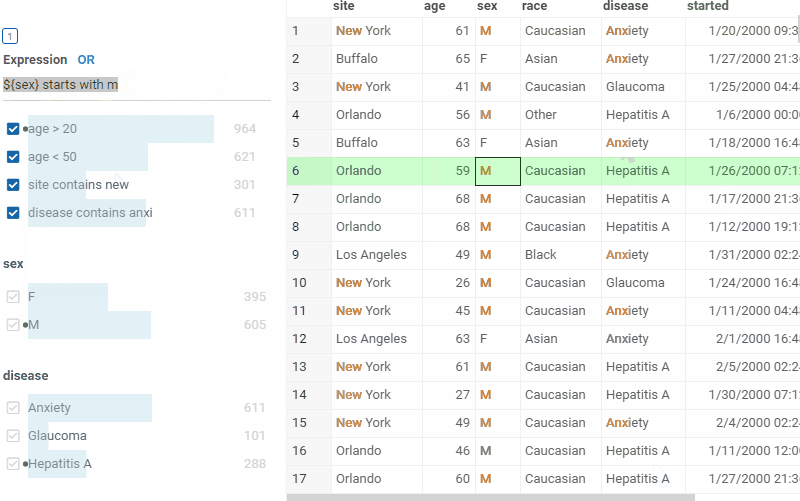
Expression filter
Expression filter lets you create custom search terms for any column. These terms are in the form of column name operation value. The following operations are supported:
- numerical columns:
none,=,!=,>,<,>=,\<=,in,not in,-,is null,is not nullage > 40height is null
- string columns:
none,contains,starts with,ends with,equals,!=,regex,in,not in,is null,is not nullrace contains sian// Asian, Caucasianrace starts with Brace in (Black, Asian)race regex ck$
- datetime columns:
none,equals,before,after,range,is null,is not nullstarted after 7/1/1991started
- bool columns:
true,false
In the filter, you can choose the column, choose available operation and value. To add expressions you can click the + button, or press enter.
Similarly to the text filter, you can control the logical operation between the expressions by using the and/or switch. In case of string columns, exact matches to the query will be highlighted in the column values.
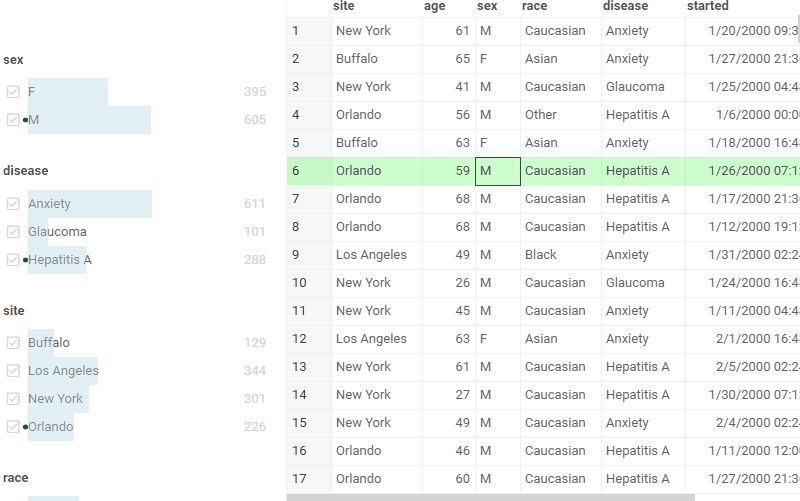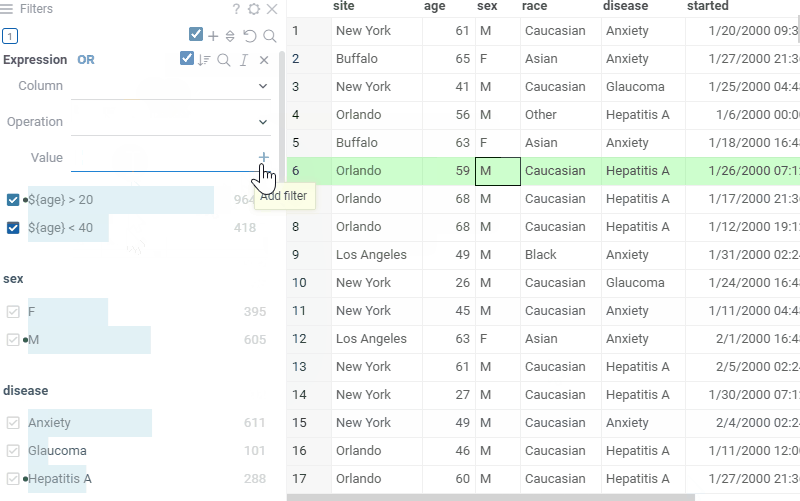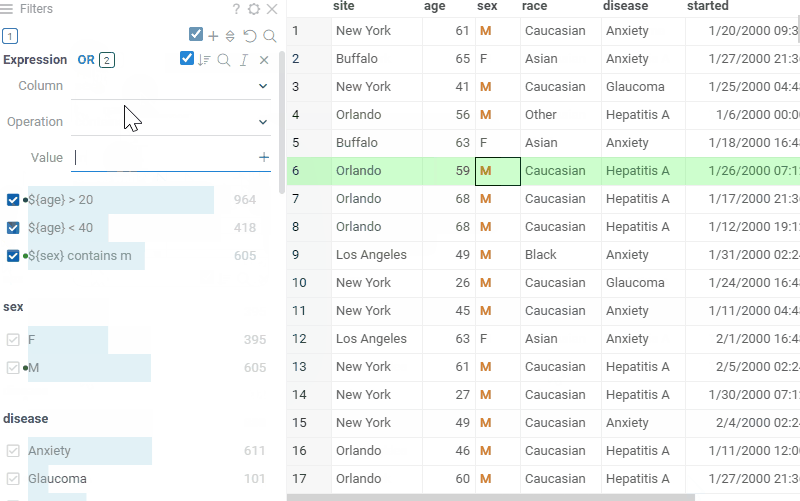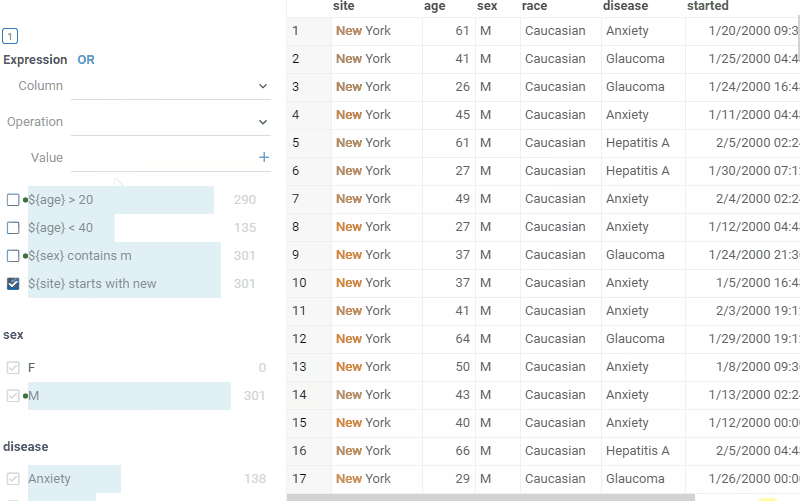
Free-text filter mode
To switch the expression filter to free-text mode, click the Free text icon on the filter. In this mode, you can enter custom search terms in a text form. The filter will parse the text and create expressions based on the entered search terms. It is also possible to use logical conditions to combine simple expressions, for example:
age > 30 and height > 190age > 30 and sex = F
In case if column name contains spaces, you can put the column name inside of escape sequence:
${column name with spaces} contains someString
Hierarchical filter
A hierarchical filter organizes column values in a tree-like structure. This filter is used for columns that have categories. For example, if the dataset contains two columns, Sex and Name, the hierarchical filter shows the values of the Name column grouped by sex categories, and each category or sub-category can be expanded, collapsed, turned on or off.
The hierarchical filter can be added from the filters hamburger menu. After the filter is added, it detects existing hierarchies based on the values (for example Country, City, Street).
- To rearrange, add or remove columns, click on the 'tree' icon in the filter, enable needed columns and arrange them in the desired order.
- To navigate around the categories/subcategories, you can use your mouse or up/down arrows.
- To expand/collapse the categories, click on the
>icon on the left of the category name or use the right/left arrow buttons. - To toggle the category, click on the checkbox on the left of the category name or use the space bar.
- To enable only one subcategory, double-click or press enter.
- To select the corresponding category/subcategory, click the corresponding count number (same as in categorical filter).
- The green and gray indicator circles to the left of category name show the current and mouse over row of the dataframe respectively.
Combined boolean filter
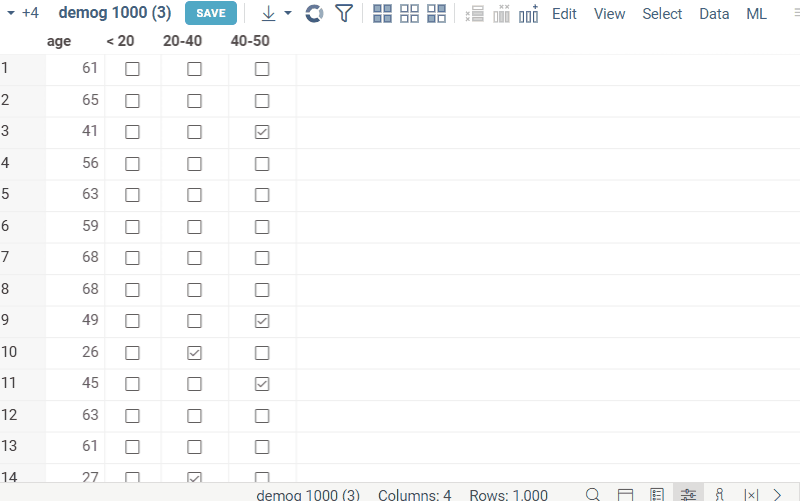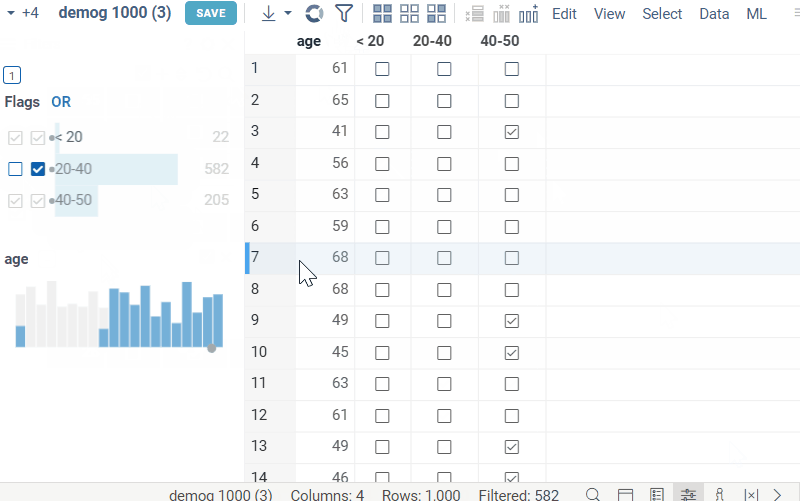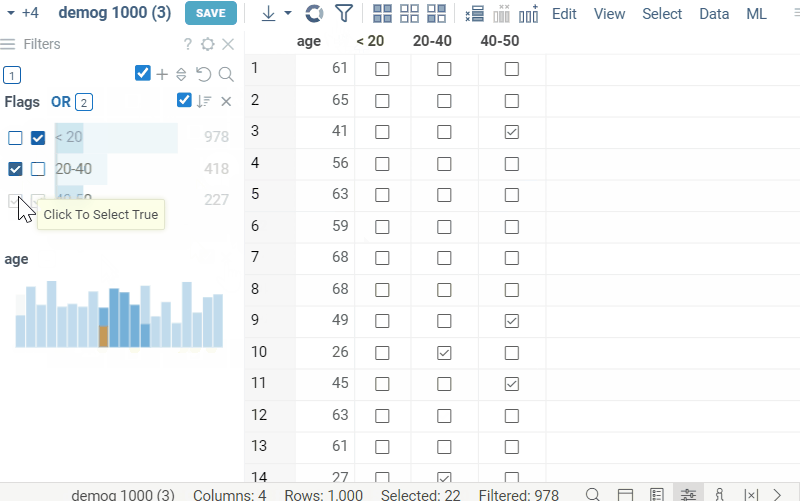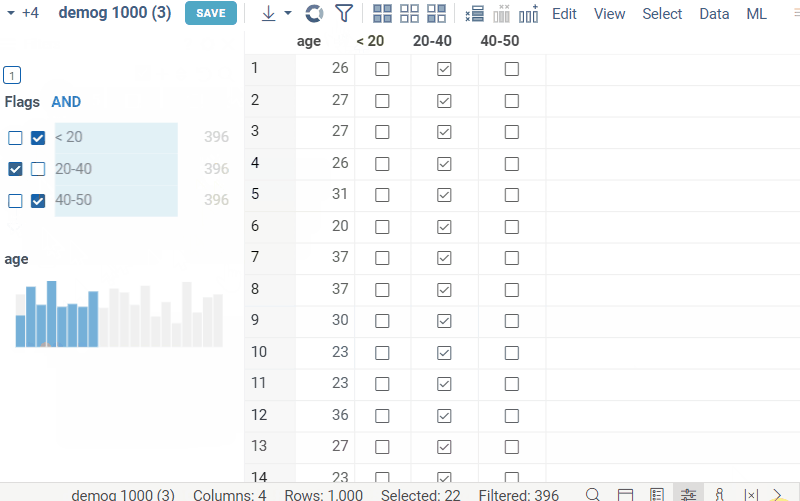
Combined boolean filter (or Flags filter) combines multiple boolean filters into one. It can be very versatile in cases where there are many boolean columns and individual filters overcrowd the filter panel. When first opening the filters panel, if dataframe contains multiple boolean columns, the combined boolean filter will be automatically created instead of separate filters for each column. Each row of the filter corresponds to a column, and contains two checkboxes, corresponding to the true and false values respectively. Applied filters can be combined using logical 'and' or 'or' operations. Like categorical filter, Flags filter includes all interactivity features, such as mouse over highlighting, selection, current row indicator, etc.
- If both checkboxes are checked in a row, the filter for that row is considered to be inactive. In this case, the value indicator of the row will show the ammount of true values in the column.
- To toggle the filter for particular row, click on the corresponding checkbox.
- To toggle the logical operation between the filters, click on the 'and/or' switch.
- To select the filtered values (true or false) for corresponding column, click the corresponding count number (same as in categorical filter).
- To navigate around the filter columns, you can use your mouse or up/down/left/right arrows.
- The green and gray indicator circles to the left of the row show the current and mouse over row of the dataframe respectively.
- If multiple boolean columns are added to the dataframe (for example by Categorize), the combined boolean filter will be automatically created.
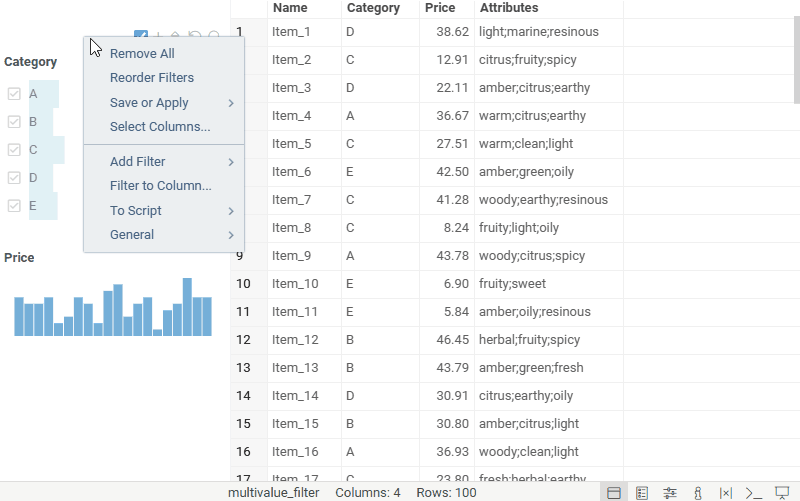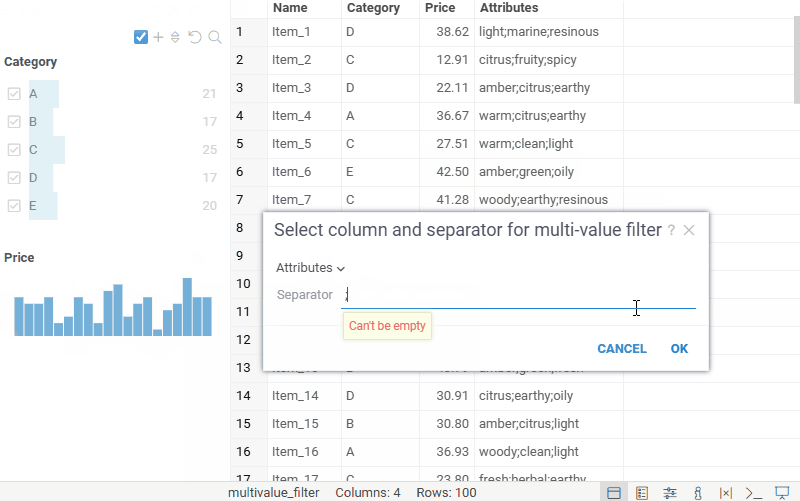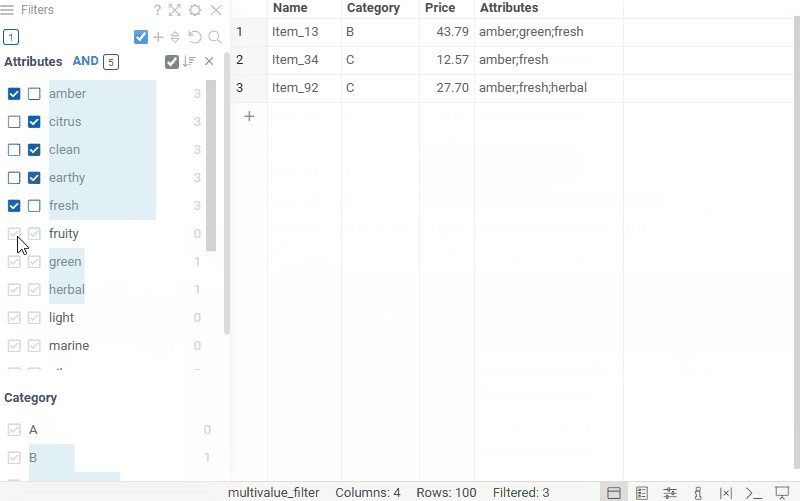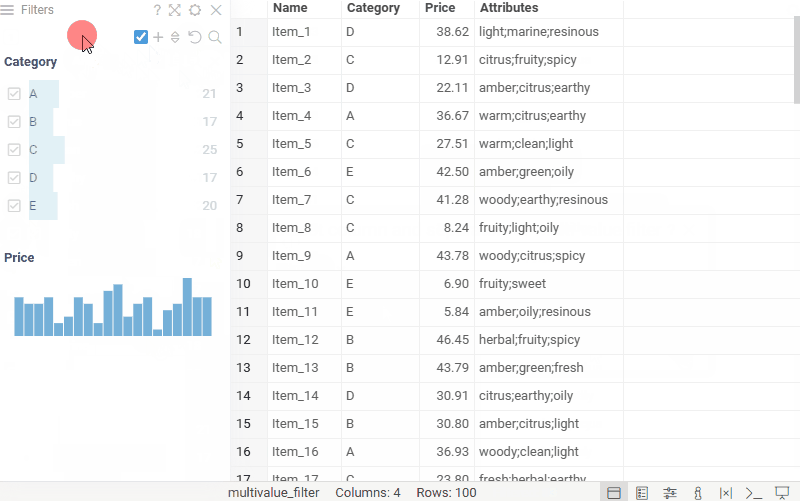
Multi-value filter
Multi-value filter lets you filter columns containing cells with multiple values, treating each value as an individual filter option. Each value in the filter has two checkboxes, allowing you to include or exclude rows that contain it. The AND/OR toggle controls how selected values are combined within the filter.
Add the filter from the Filter Panel hamburger menu: Add Filter > Multi Value....
Once added, the multi-value filter uses the .multiValueSeparator column tag
to split values in the selected column.
Saving a filter configuration
You can save a filter configuration for later use:
- In the Filter Panel context menu, select Save or Apply > Save…
- Enter a name for the saved configuration.
Restore this configuration through Save or apply in the context menu.
Column tags
-
For molecular columns, use the .structure-filter-type column tag to define filter type:
- Set .structure-filter-type to
Sketchto use Sketcher for filtering molecular columns. - Set .structure-filter-type to
Categoricalto use molecular column values as categories in the filter group.
- Set .structure-filter-type to
-
For multi-value columns, use the column.meta.multiValueSeparator to parse multiple values as separate filter categories. The most common separators are
\n,,,;.Example
t.col('languages')meta.multiValueSeparator = '\n';
-
To work with custom filters, use such column tags as
.custom-filter-typeand.ignore-custom-filter. The.custom-filter-typetag contains a custom filter name to be used by default for a column. Its value consists of two parts: the namespace and the function name (<PackageName>:<FilterType>, e.g.,Chem:substructureFilter). Use the.ignore-custom-filtertag to control custom filters visibility. If both tags are used,DG.TAGS.CUSTOM_FILTER_TYPEtakes precedence overDG.TAGS.IGNORE_CUSTOM_FILTER.
To set the column tag value via the UI:
- Right-click the column's header and select Column Properties from the context menu. A dialog with column metadata opens.
- In the dialog, use the Plus icon to add a new tag.
- Enter the tag name and value.
- Click OK to save changes.
To set the column tag value programmatically:
column.tags[DG.TAGS.STRUCTURE_FILTER_TYPE] = 'Categorical';
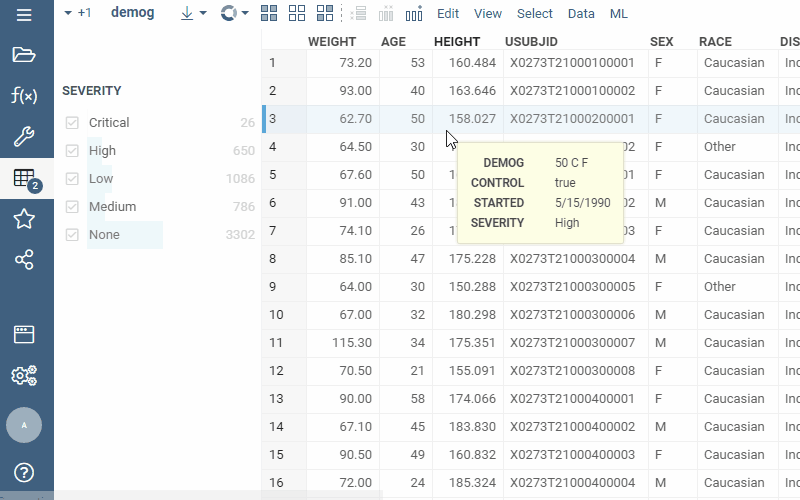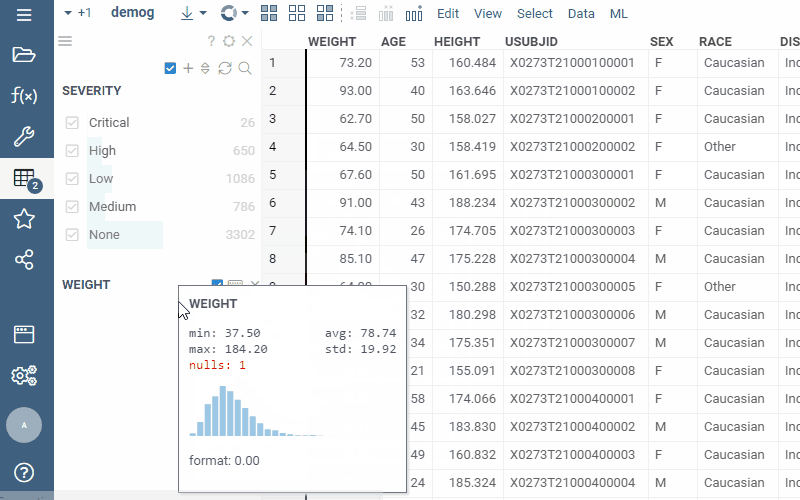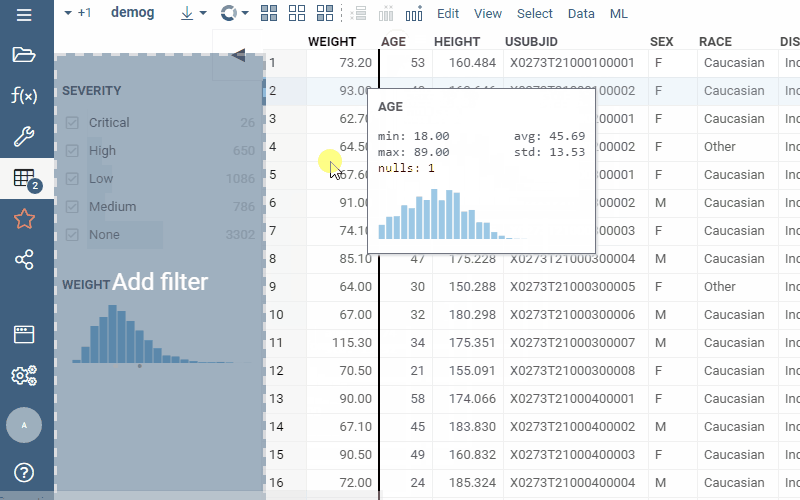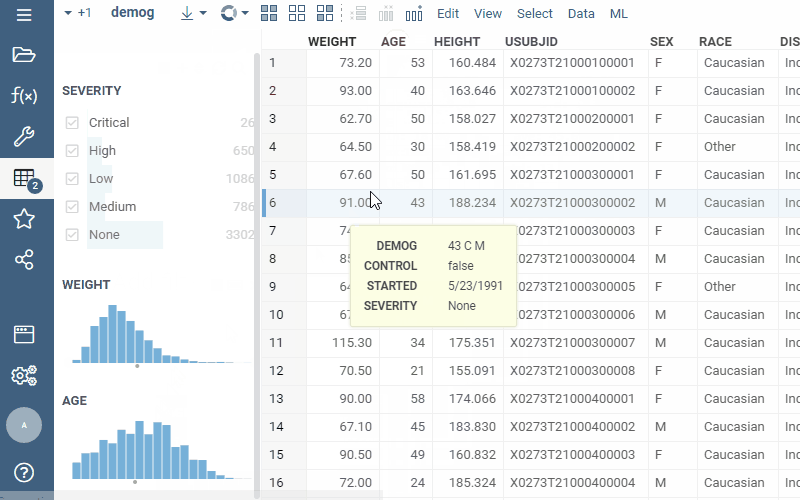
Drag-and-drop
Drag-and-drop columns right from the grid to add the corresponding filters:
Properties
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General | ||
| Histogram Look | histogramlook | |
| Show Filter Counts Indication | boolean | |
| Show Filter Indication | boolean | |
| Show Selection Indication | boolean | Indicate the proportion of the selected rows inside each category. |
| Show Header | boolean | |
| Show Histogram | boolean | |
| Show Min Max | boolean | |
| Show Search Box | boolean | |
| Show Mouse Over Row | boolean | shows the current mouse over row in the table using grey vertical bar in corresponding row |
| Show Current Row | boolean | shows the current row in the table using green vertical bar in corresponding row |
| Show Mouse Over Group Row | boolean | shouws the mouse over group porportion in the filter (similar to how selection proportion is shown). |
| Show Bool Combined Filter | boolean | Show a filter that represents all boolean columns in the table. |
| Column Names | list | |
| Filters | list | |
| Allow Dynamic Menus | boolean | |
| Show Context Menu | boolean | Properties common for all viewers todo: use code generation |
| Title | string | |
| Description | string | Viewer description that gets shown at the Descriptor Position. Markup is supported. |
| Help | string | Help to be shown when user clicks on the ''?'' icon on top. Could either be in markdown, or a URL (starting with ''/'' or ''http''). |
| Description Position | flexposition | |
| Description Visibility Mode | visibilitymode | |
| Description | ||
| Show Title | boolean | |
| Data | ||
| Table | string |
See also: